Policy Update
Bhavana Girase
Background
Agriculture is the backbone of India’s economy and also the primary source of livelihood. It falls under the primary sector and supplies raw material to various other sectors. Therefore, the growth and modernisation of this sector are essential for the overall development of the nation. With this purpose, the Department of Agriculture Research and Education (DARE) was established in December 1973 under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare to strengthen agricultural research and education. It plays a pivotal role in formulating policies and promoting innovations. DARE’s Vision and Mission highlight the core objectives, which are as follows:

Source: Department of Agriculture Research and Education
The primary motto of the DARE is to make the country self-reliant in the agriculture sector.
DARE has the following four autonomous bodies under its administrative control:
1.Indian Council Of Agriculture research (ICAR), New Delhi
2.Central Agricultural University, Imphal, Manipur
3.Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, Pusa, Bihar
4.Rani Laxmi Bai Central Agricultural University, Jhansi, UP
DARE also serves as the nodal agency for international cooperation in the field of agriculture research and education in India. Additionally, it coordinates the admission of foreign students to various Indian agricultural universities.
Functioning
- The main function of DARE is to maintain coordination between central and state agencies while overseeing various aspects of agricultural research.
- DARE develops national policies on agricultural research and also encourages research in crop improvement, climate resilience, livestock, fisheries and natural resource management.
- DARE coordinates and supports the activities of the Indian Council Of Agriculture Research, the primary implementing body for agriculture research and education.
- DARE also provides budgetary support for agricultural research and development, which promotes technological development in agriculture, horticulture, agricultural extension, animal science, economic statistics and marketing and fisheries.
- DARE builds partnerships with international organisations and promotes international cooperation by encouraging foreign students to pursue agricultural research and education in India.
DARE coordinates with the following organisations to ensure effective functioning:
Indian Council Of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi
ICAR is an autonomous organisation DARE. It was established on 16th July 1929 as a registered society. It is the apex body for coordinating, guiding and managing agriculture research and education across the country, covering areas of horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences.
Central Agricultural University (CAU), Imphal, Manipur
Established on 26th January 1993, by an Act of Parliament. It is a fully residential institution headquartered in Imphal, Manipur. It integrates teaching, research, and extension education. It plays an important role in fostering innovation and sustainable development in the North-East region of India.
Dr.Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, Pusa, Bihar
Originally established 1970 at Pusa. It is India’s first agricultural university and has become an important landmark in agricultural research and education in the eastern region of the country. It has also received national recognition for various initiatives, including DGCA-approved Drone Pilot Training Center and the inauguration of a 5G Lab by the Hon’ble Prime Minister in 2023.
Rani Laxmi Bai Central Agricultural University, Jhansi, UP
Established on 5th march 2014, this is India’s second central agricultural university. Named in memory of Queen of Jhansi Late Rani Laxmi Bai. It was established with the purpose of imparting quality education and overall improvement in the quality of life of the farming community in the Bundelkhand region.
Agrinnovate India Ltd
A registered company under companies act 1956. Agrinnovate works on the strengths of DAREs ICAR to promote the development and commercialization of R&D. It focuses on IPR protection and is mandated with stimulating and fostering innovations in agriculture and works as an important interface between the research institutes.
Agricultural Scientists Recruitment Board (ASRB)
Established on 1st November 1973 as an independent recruitment agency as per recommendations of the Gajendragadkar Committee. Delinked from ICAR, ASRB now functions under DARE with its own Cadre of administrative staff and a separate budget. It is responsible for recruiting scientific personnel for agricultural research.
Indian Agricultural Universities Association (IAUA)
Established on 10th November 1967. IAUA promotes agricultural research, education and extension among universities and states. It also acts as a bureau of information to facilitate communication, co-ordination and mutual consultation among agricultural universities and also acts as a liaison with government departments.
National Academy Of Agricultural Sciences(NAAS)
Established on 5th June 1990, NAAS serves as a think tank and forum for advancing science in agriculture. It focuses on enhancing the productivity, profitability, equity and sustainability of Indian agriculture and the related policies leading to a comprehensive food nutrition livelihood-ecology-secured and climate-smart India.
Consultative Group On International Agricultural Research (CGIAR)
CGIAR is a global partnership that unites international organizations engaged in research for food security in the future and dedicated to reducing rural poverty, increasing food security, improving human health and nutrition and ensuring sustainable management of natural resources. India is a donor member.
Performance
DARE contributes significantly through innovations in climate-resilient technologies, digital agriculture and modernisation of agricultural practices. The key performance highlights are as follows:
Institutional Network Expansion-With a vast network 113 ICAR institutions and 74 Agricultural universities. India has one of the largest national agricultural systems in the world. This network plays a major role in promoting excellence in higher education and thus contributes to food and nutritional security.
Increased Farmers Outreach-A network of 731 Krishi Vigyan Kendras(KVKs) that bridge the gap between research and practice by bringing innovations directly to farmers field.
Climate Resilience-Development and promotion of climate-resilient crop varieties, integrated pest management, integrated farming system and conservation agriculture technique.
Crop Improvement-Research in genetically improved seeds, gene editing, biofortified varieties for enhanced nutrition and pest resistance which include 35 biofortified varieties like zinc-rich wheat and iron-rich millet (Pusa Basmati 1121 and HD-3226 Wheat)
Technological Advancement-Leveraging modern technologies like IoT sensors, drone, satellite imagery, mobile app like KISAAN Suvidha and mKisan for real-time monitoring of crop health, soil conditions, weather patterns.
Water Management Innovations-Promoting sustainable water use through drip irrigation, micro-sprinklers, sensor-based water application and satellite soil moisture monitoring.
Sustainable & Organic Farming-Promotion of organic farming, Bio-fertilizers, Bio-pesticides, Ethanol Procurement and climate smart solutions to reduce environmental hazards.
Ensuring Food Security- India has achieved self-sufficiency in cereals, pulses, oilseeds, milk and fisheries through transformative innovations such as Green Revolution and Milk Revolution played an important role.
Modernising Agricultural Markets- National Agriculture Market(e-NAM), which digitally links mandis and the promotions of Farmer Producer Organisation. Other initiatives such as Soil Health Card, Kisan Credit Card, Agri-Export Hubs and Mega Parks.
Agriculture Diversification- To increase farmers income and ensure sustainability DARE supports horticulture, ethanol procurement, livestock poultry and fisheries.
Knowledge & Capacity Building- Using digital platforms and live demonstration to train students, scientists and farmers.
International Cooperations- DARE actively engages in multilateral international collaborations in agricultural research. Major partnerships include:
- DARE role towards cooperation in SAARC, BRICS, BIMSTEK, ASEAN and G20
- Asia-Pacific Association of Agricultural Research Institutions
- International Society for Horticultural Sciences
- International Seed Testing Association
- CABI (Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International)
- UN Asian and Pacific Centre for Agricultural Engineering and Machinery
- International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
Key Performance Indicators At A Glance:


Source: Press Information Bureau(PIB)
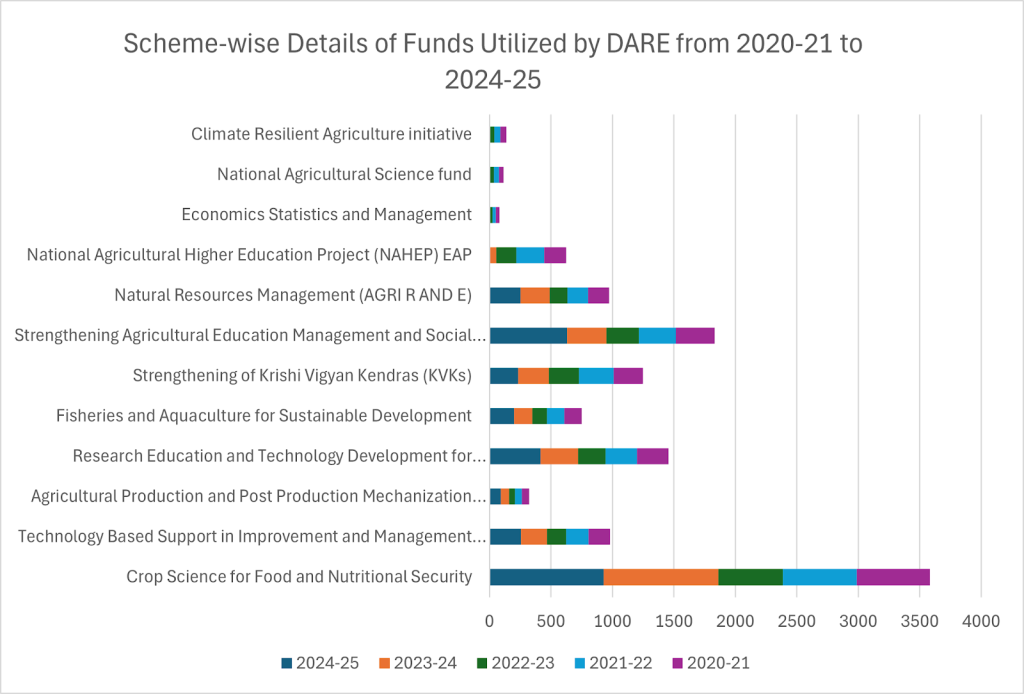

Source: Open Government Data (OGD)
Impact
DAREs focused efforts have significantly transformed Indian agriculture and strengthened agriculture research through ICAR institutes which leads to improve following aspects:
Food System Transformation-Improved food production, nutrition and human health, adaptation to climate change, sustainable resource use and promotion of food safety, small business innovation and workforce development.
Crop Varieties- Improved crop varieties to combat the various abiotic stresses like drought, water scarcity, flood, waterlogging, salinity, low temperature etc.
Livestock Research Development- Opens new avenues for India’s dairy sector, offering advanced reproductive technologies to produce high quality indigenous dairy animals.
Smart Agriculture- Pursued the deployment of digital platforms in agriculture and the application of ICT for farmers’ empowerment.
Training and Capacity Building- Hands-on training and technical guidance to farmers from across the country on induced breeding, hatchery management, seed production and live feed culture.
Soil and Water Productivity- Development of soil health management practices to improve soil fertility and enhancing water-use efficiency.
Public-Private Partnership- Encouraged for faster commercialization of innovations.
Exchange of Knowledge – To enhance agricultural research and education actively participation globally.
Emerging Issues
Despite progress, Indian agriculture faces several pressing challenges:
Climate Change- Leads to unpredictable monsoons, droughts, floods and rising temperature impacting crop yields.
Excessive Fertilization-Degrading soil health, decrease productivity and causing environmental hazards
Excessive Water Use-Leading to salinity of soil and depletion of groundwater level
Market Fluctuations & Storage Issues-Unstable prices and storage issues result in food wastage, loss of farmers income and post-harvest losses.
Technical & Resource Gaps- Due to limited digital literacy and infrastructural gaps and challenges in agri-tech adopting.
Way Forward
To achieve the vision of Vikshit Bharat @2047, India must transform its agriculture into a sustainable, inclusive, technology-driven and farmer centric sector. In this direction, ICAR has initiated work across five key dimensions-making agriculture more science based, technology enabled, market friendly, women friendly and culture friendly. These efforts mark a significant step toward building a self-reliant and inclusive agricultural system for the future.
References
Open Government Data(OGD) Scheme-wise Details of Funds Utilized under Schemes Implemented by Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE) from 2020-21 to 2024-25 https://www.data.gov.in/resource/scheme-wise-details-funds-utilized-under-schemes-implemented-department-agricultural
Department of Agriculture Research and Education(DARE).Annual Report 2023-24. https://dare.gov.in/ https://dare.gov.in/storage/pdfs/DARE%20English%20Annual%20Report%202023-24.pdf
Indian Council of Agriculture Research(ICAR).Annual Report 2023-24. https://icar.org.in/sites/default/files/2025-04/ICAR%20Annual%20Report%202023-24-english.pdf
About The Contributor
Bhavana Girase is a Research Intern at Impact and Policy Research Institute(IMPRI). A data and policy research enthusiast, with a background in UPSC preparation and focusing on turning complex data into interpretative insights for better understanding of policies.
Acknowledgement
The author sincerely thanks Ms.Aasthaba Jadeja and the IMPRI team for their valuable support and guidance.
Disclaimer
All views expressed in the article belong solely to the author and not necessarily to the organisation.
Read More on IMPRI
Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs): Knowledge to Field (2025)
Farmer Producer Organizations: A Pathway to Rural Prosperity (2025)



















