Policy Update
Chetan Gupta

Introduction
India and Qatar share historic trade linkages, deep-rooted people-to-people ties and robust multifaceted bilateral relations. Qatar and India established diplomatic relations in the early 1970s. They celebrated 50 years of diplomatic ties in 2023. The most recent visit by the Amir of Qatar, Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani, to India in February 2025 upgraded the relations between the two countries to a Strategic Partnership. They have signed the “Agreement on the Establishment of Bilateral Strategic Partnership”, which included a pledge of USD $10 billion of Qatari investment in India. The two sides reaffirmed their commitment to strengthening bilateral relations through regular and structured cooperation.
Background
The India-Qatar trade relationship has been a strong pillar of bilateral economic cooperation. Most significantly, liquefied natural gas (LNG) is the predominant backbone of trade ties. Qatar has the world’s third-largest natural gas reserves; at the same time, India is the fastest-growing energy market globally because of increased demand for cleaner energy sources. Qatar is now India’s largest and dominant supplier of LNG, accounting for 40 per cent of the country’s total LNG imports. It makes up almost 50% of overall Indian imports (by value) from Qatar. The energy partnership started in the 1990s, and last year Qatar Energy and India’s Petronet LNG Ltd signed a 20-year agreement, which will further strengthen trade ties.


Amir of Qatar Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani and Prime Minister Narendra Modi during State Visit of India 2025 (Source: The Indian Express)
The two sides are exploring the possibility of entering into a bilateral Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement. Both sides set the target to double bilateral trade to around $28 billion annually by 2030. Qatar is pursuing the Qatar National Vision 2030 (QNV 2030) framework to develop its economy. The initiatives, for instance, the opening of the Qatar Investment Authority’s (QIA) office in India, the commitment to invest US$10 billion in India and the recent inauguration of the Joint Business Forum, demonstrate the keen interest of Qatar in India’s growth and development potential.
Objectives
The bilateral gas trade has particular objectives:
- India’s energy security and reduce its dependence on oil imports.
- Stable and reliable LNG supplier for India’s increasing energy demands and economic growth.
- India’s transition towards a lower-carbon economy.
- Qatar’s economic diversification by establishing long-term LNG export markets.
- The establishment of strategic ties and economic cooperation through energy diplomacy.
Functioning
Gas trade between India and Qatar is facilitated hrough long-term LNG supply contracts and infrastructure investments. State-owned entities (e.g. Petronet LNG, GAIL, Qatar Energy, etc.) play an indispensable role in LNG trade. Qatar is a stable and reliable energy supplier to India, contributing to its energy security and supplying about 40% of its LNG imports. India has increasingly diversified its LNG supply sources in recent years. In 2016, 60% of India’s LNG imports came from Qatar, down from 85% in 2014. Other sources of India’s LNG include the United States, the UAE, Angola, and Nigeria.
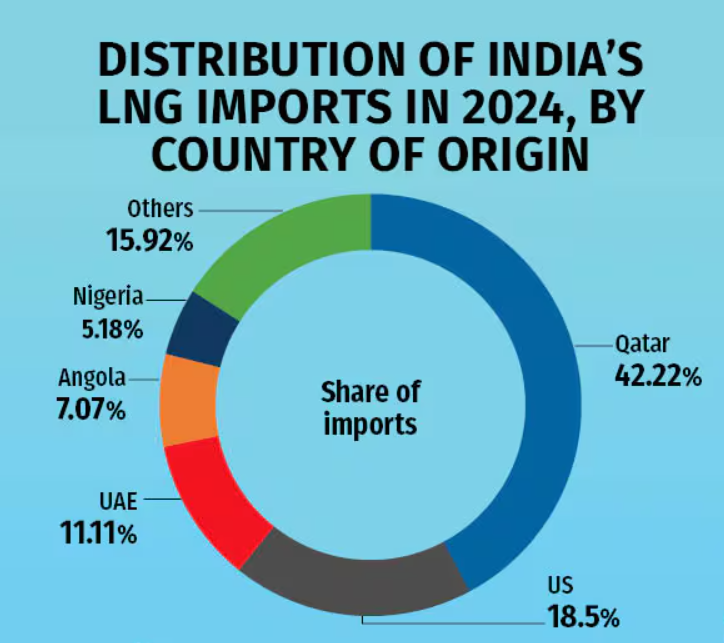

Distribution of India’s LNG Imports in 2024, by Country of Origin (Source: Moneycontrol)
Natural gas is a cleaner alternative to conventional petroleum fuels (diesel and petrol) and cheaper than crude oil. India has an import dependency of over 85% on crude oil. Hence, gas is affordable and a better fuel for the energy transition pathway.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), India’s LNG imports are set to more than double between 2023 and 2030 to 65 billion cubic metres (bcm) a year, driven by steady demand growth and a much slower rise in domestic production. Between 2013 and 2023, India’s LNG imports increased by 70% and reached 36 bcm in 2024, cementing the country’s position as the fourth-largest LNG importer globally. Qatar emerged as a major player for India’s LNG imports as it has an advantageous geographical location in the Middle East and globally, a low unit cost of LNG production (ensuring profitability amid volatility), and tremendous LNG production capacity (third globally).
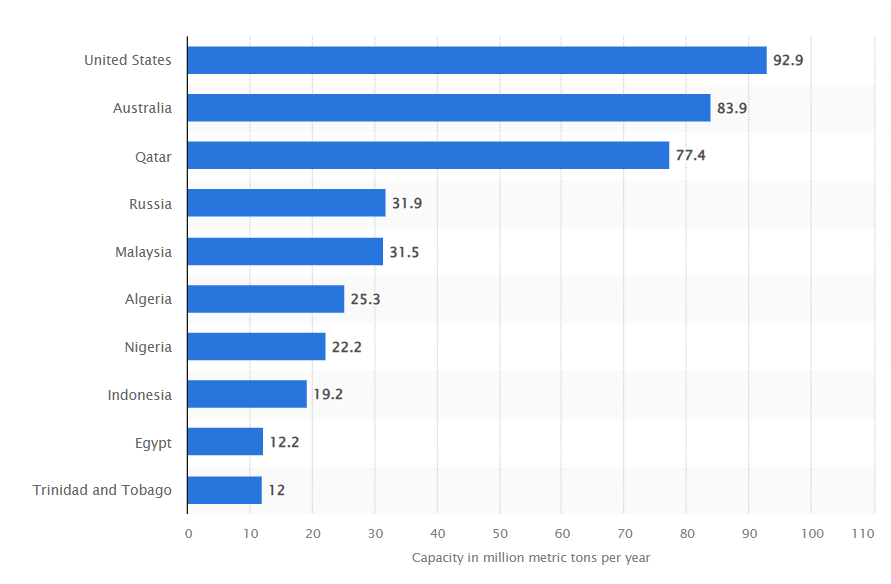

Countries with largest LNG export capacity in operation worldwide (2024) (Source:Statista)
Performance
India’s bilateral trade with Qatar in 2023-24 was USD $14.08 billion. India’s export to Qatar during the period was USD $1.7 billion, and India’s import from Qatar was USD $12.38 billion. India is Qatar’s second-largest trading partner, among the top four sources of Qatar’s imports. The balance of trade continues to be heavily in Qatar’s favour. However, India’s exports to Qatar have grown substantially in the last few years in diversified areas. India imported 19.85 million tonnes of LNG in FY23, of which 10.74 million tonnes, or 54%, came from Qatar (additional purchase than the agreement).
Table: Imports from Qatar to India 2023-24 (Source: MEA, GOI)
| Products Imported from Qatar | Value (USD million) |
| LPG, LNG, Crude oil | 11,009.06 |
| Organic Chemicals | 388.53 |
| Plastics | 316.27 |
| Aluminium | 159.55 |
| Fertilisers | 155.78 |
| Inorganic chemicals | 114.79 |
| Misc. Chemical Products | 80.68 |
| Gems and Jewellery | 37.59 |
| Salt, Sulphur, Lime, Cement | 26.86 |
| Ships, Boats and floating structures | 20.66 |
In February 2024, India and Qatar signed a long-term agreement worth USD $78 billion to export 7.5 million tonnes of Qatar’s LNG to India annually for 20 years, starting in 2028. The first 25-year deal is to expire in 2028. The agreement aims to support India’s energy transformation with a consistent and reliable cleaner supply. Both countries are interested in enhanced energy cooperation, as India is targeting a 15% (from 6%) share of gas in its energy mix by 2030 to meet increasing demand and infrastructure needs. Simultaneously, Qatar will inaugurate landmark projects to raise its local and international LNG production to 160 million tonnes annually (MTA) in a few years from the current output of 77 MTA.


LNG Tanker used for bulk Transportation (Source:Moneycontrol)
Impact
The Russia-Ukraine war has disrupted the global LNG market, causing sharp price volatility. This has made long-term contracts, like the one Petronet has with Qatar, a more viable option to ensure stable LNG supply.
Because of India’s dependency on LNG imports and Qatar being the predominant supplier of LNG in the global market, their energy ties strategically complement each other. The recent state visit has emphasised the role of the Joint Task Force on Energy, which aims to promote trade and mutual investment in energy infrastructure. In February 2025, both sides inaugurated the Joint Business Forum and elevated the existing Joint Working Group on Trade and Commerce into a Joint Commission on Trade and Commerce. The Qatar side expressed interest in exploring investment opportunities in different sectors, including infrastructure, technology, manufacturing, food security, logistics, hospitality, and other areas of mutual interest.


LNG Storage Tanks (Source:Moneycontrol)
Emerging Issues
- India has low domestic gas production and infrastructure disparities across regions (e.g. central and southern India), which become a challenge for self-reliance in energy.
- The LNG market has pricing, regulatory and affordability challenges. This controlled pricing and limited access to private players are issues in this sector.
- Qatar’s expanding LNG production capacity and India’s increasing imports require robust infrastructure expansion.
- To achieve carbon reduction targets, there must be a balance between continued LNG imports and the scaling up of renewable energy.
- The gas trade faces significant challenges, including geopolitical tensions in the Strait of Hormuz and global energy price fluctuations.
Way Forward
The leaders of both countries have recently stated that “there is both the will and potential” in the two countries to boost and diversify mutual trade and investment ties. India’s LNG imports are expected to surge in the upcoming years as the country’s natural gas consumption is set to grow exponentially. Moreover, the expected import growth would coincide with Qatar’s expanding LNG export capacity.
India needs to bring reforms to expand its gas pipeline network nationwide. There is a need to increase investment in LNG infrastructure (e.g. expanding storage, regasification terminals, and city gas distribution). Both countries can explore collaborating in renewable energy, such as hydrogen, solar, and wind energy, whereas Qatar can invest in India’s clean energy projects. India should reduce its reliance on a single dominant LNG supplier by increasing energy partnerships with other nations. India’s energy security is directly linked to its economic growth and climate goals—Qatar’s expansion of LNG exports and economic diversification support India’s energy transition. The trade relationship between the two countries signifies an intersection of economic, strategic and environmental objectives.
References
- Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). (2025, February 11). India–Qatar Relations: Brief. Retrieved from https://www.mea.gov.in/Portal/ForeignRelation/brief-11-Feb-2025.pdf
- Ministry of External Affairs (MEA). (2025, February 18). India–Qatar Joint Statement. Retrieved from https://www.mea.gov.in/bilateral-documents.htm?dtl/39083/India++Qatar+Joint+Statement+February+18+2025
- Observer Research Foundation (ORF). (2025, May 19). India and Qatar at 50: A Strategic Partnership for a New Era. Retrieved from https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/india-and-qatar-at-50-a-strategic-partnership-for-a-new-era
- Indian Express. (2023, October 28). How Natural Gas is central to the ties between India and Qatar. Retrieved from https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/natural-gas-lng-india-qatar-relations-9002396/
- Indian Express. (2025, February 19). India and Qatar Elevate Ties in Trade, Energy and Investment. Retrieved from https://indianexpress.com/article/india/india-and-qatar-elevate-ties-in-trade-energy-and-investment-9843497/
- Indian Express. (2025, February 19). As India and Qatar eye Trade Expansion, why LNG’s centrality in bilateral trade is in focus. Retrieved from https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/india-qatar-trade-lng-significance-9848542/
- Indian Express. (2025, February 20). Sheikh Al-Thani Visits India: New Delhi’s Qatar Opportunity, in trade and geopolitics. Retrieved from https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/an-expert-explains-indias-qatar-opportunity-9845347/
- Hindustan Times. (2025, February 19). India, Qatar to Double Trade to $28 Billion in Next Five Years. Retrieved from https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/india-qatar-to-double-trade-to-28bn-in-next-five-years-101739902852505.html
- Economic Times. (2024, February 6). India saves $6 bn on Qatar LNG deal renewal; signs $78 billion pact for 20 years. Retrieved from https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/energy/oil-gas/india-likely-to-extend-lng-import-deal-with-qatar-for-20-years-at-lower-rates/articleshow/107445186.cms?from=mdr
- Economic Times. (2025, February 17). From Energy to Diplomacy: Exploring the Multifaceted India–Qatar Relationship. Retrieved from https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/from-energy-to-diplomacy-exploring-the-multifaceted-india-qatar-relationship/articleshow/118317621.cms?from=mdr
- Kute Pratik. (2018). Qatar-India Energy Ties: Emerging Opportunities and Challenges. World Affairs: The Journal of International Issues, vol. 25, no. 4, 2021, pp. 90–103. JSTOR. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/48654882
- International Energy Agency (IEA). (2021). India Gas Market Report 2021. Retrieved from https://iea.blob.core.windows.net/assets/ef262e8d-239f-4cfc-8f8c-4d75ac887a0f/IndiaGasMarketReport.pdf
- NITI Aayog & International Energy Agency (IEA). (2020). India Energy Policy Review 2020. Retrieved from https://niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2020-01/IEA-India-In-depth-review2020.pdf
- Moneycontrol. (2025, June 23). Half of India’s LNG imports come from Qatar and UAE, relying on Strait of Hormuz for supplies. Retrieved from https://www.moneycontrol.com/news/business/economy/half-of-india-s-lng-imports-come-from-qatar-and-uae-relying-on-strait-of-hormuz-for-supplies-13165176.html
About the contributor: Chetan Gupta is a Research Intern at Impact and Policy Research Institute (IMPRI). He is currently pursuing his MA in International Relations from the Department of International Relations, South Asian University (established by SAARC nations), Delhi. His research areas are International Relations and Public Policy.
Acknowledgement: The author sincerely thanks Ms. Aasthaba Jadeja and the IMPRI team for their valuable support.
Read more at IMPRI:
Another Policy, Same Mistake: The GST Rate Cut Echoes Demonetisation’s Flaws
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK) – Model Training Centres (2025)



















